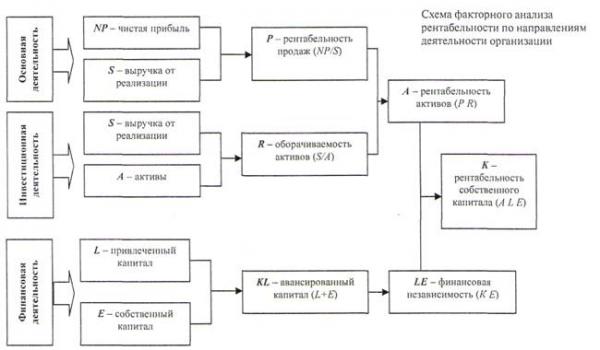
Operating margin
Содержание:
- Net Profit Margin
- Что такое маржа в деятельности предприятия?
- Валовая маржа
- Маржа и валовая прибыль: в чем разница
- Operating Cash Flow Margin vs. Operating Margin
- Operating Cash Flow Margin Example
- Увеличение маржи операционной прибыли
- Gross Margin vs. Contribution Margin Example
- Types of Profit Margin
- Understanding the Operating Cash Flow Margin
- What Is Operating Margin?
- Understanding Operating Margin
- How to calculate net profit margin
- Основные виды
- About This Article
- Другие виды маржи
- Comparing Gross Margin and Operating Margin
- Hypothetical Example
- Analysis
Net Profit Margin
Let’s now consider net profit margin, the most significant of all the measures—and what people usually mean when they ask, «what’s the company’s profit margin?»
Net profit margin is calculated by dividing the net profits by net sales, or by dividing the net income by revenue realized over a given time period. In the context of profit margin calculations, net profit and net income are used interchangeably. Similarly, sales and revenue are used interchangeably. Net profit is determined by subtracting all the associated expenses, including costs towards raw material, labor, operations, rentals, interest payments, and taxes, from the total revenue generated.
Mathematically, Profit Margin = Net Profits (or Income) / Net Sales (or Revenue)
= (Net Sales — Expenses) / Net Sales
= 1- (Expenses / Net Sales)
NPM =(R − COGS − OE − O − I − TR) ×1orNPM = (Net incomeR)×1where:NPM=net profit marginR=revenueCOGS=cost of goods soldOE=operating expensesO=other expensesI=interest\begin{aligned} &\begin{gathered} \textit{NPM }=\left(\frac{\textit{R }-\textit{ COGS }-\textit{ OE }-\textit{ O }-\textit{ I }-\textit{ T}}{\textit{R}}\right)\ \times100\\ \textbf{or}\\ \textit{NPM }=\ \left(\frac{\textit{Net income}}{\textit{R}}\right)\times100 \end{gathered}\\ &\textbf{where:}\\ &NPM=\text{net profit margin}\\ &R=\text{revenue}\\ &COGS=\text{cost of goods sold}\\ &OE=\text{operating expenses}\\ &O=\text{other expenses}\\ &I=\text{interest}\\ &T=\text{taxes} \end{aligned}NPM=(RR−COGS−OE−O−I−T)×1orNPM=(RNetincome)×1where:NPM=net profit marginR=revenueCOGS=cost of goods soldOE=operating expensesO=other expensesI=interest
Dividends paid out are not considered an expense, and are not considered in the formula.
Taking a simple example, if a business realized net sales worth $100,000 in the previous quarter and spent a total of $80,000 towards various expenses, then
Profit Margin = 1 — ($80,000 / $100,000)
= 1- 0.8
= 0.2 or 20%
It indicates that over the quarter, the business managed to generate profits worth 20 cents for every dollar worth of sales. Let’s consider this example as the base case for future comparisons that follow.
Что такое маржа в деятельности предприятия?
Это оценочная величина. Ее значение может выражаться в процентах или в денежном эквиваленте, причем валюта может быть любой. Очевидно, что для российских компаний наиболее распространенным способом является подсчет значения в рублях. Фактически, он демонстрирует каков объем реальной прибыли, полученной компанией от реализации продукции. В большинстве случаев переменные затраты (находящиеся в зависимости от объема товара) на ее производство не учитываются.
Особенную важность подсчет показателя приобретает в области торговли, поскольку помогает без привлечения сложной математики реально оценить насколько эффективно велась та или иная деятельность. Кстати, значение маржи понадобится вам и при расчете рентабельности
Чтобы получить объективный показатель, нужно высчитать соотношение прибыли с суммой выручки, а затем умножить на 100%
Кстати, значение маржи понадобится вам и при расчете рентабельности. Чтобы получить объективный показатель, нужно высчитать соотношение прибыли с суммой выручки, а затем умножить на 100%.
Для анализа эффективности предприятия обычно менеджеры прибегают к изучению валовых показателей. Они дают возможность получить менее детальные результаты, но неплохо иллюстрируют общую картину и направление движения развития предприятия. Валовую маржу можно вычислить путем подсчета разницы между суммой выручки, полученной от реализации товара, и расходами на изготовление. Зная ее значение, можно рассчитать чистую прибыль компании или процент рентабельности продаж.

фото с сайта rarf.ru
Данные относительного выражения валовой маржи требуются для принятия управленческих решений. Хороший управленец знает цену такого анализа и не пренебрегает им. Именно этот индикатор является ключевым фактором, определяющим ценообразование. В зависимости от него находится рентабельность затрат на маркетинг, прогноз выгоды и оценка потенциальной прибыльности того или иного клиента.
Валовая маржа
Если в предыдущем примере мы считали маржу на единицу продукции, а наше производство изготовило и продало несколько партий этой продукции, то считать мы будем уже валовую маржу.
Расчет валовой маржи происходит по аналогичной формуле:
((Валовый Доход — Валовая Себестоимость)/Валовый Доход) × 100
Пример
Вы продали 150 банок варенья по цене 130 руб. за банку. Купили вы эти 150 банок варенья у производителя по цене 50 руб. за банку и еще потратились в размере 500 руб. на логистику товара.
Вопрос: какова валовая маржа вашей сделки?
- Валовая себестоимость = 150 × 50 + 500 = 8000 руб.
- Валовый доход = 150 × 130 = 19 500 руб.
- Валовая маржа = ((19 500 — 8000) / 19500) × 100 = 58,9%
- Валовая маржа вашей сделки составила 58,9%
Как правило, цифры процента валовой маржинальности меньше, чем при расчете маржи на единицу продукции. Это естественно, поскольку издержки производства, хранения, рекламы, доставки и пр. на крупные партии товаров выше, а значит, выше себестоимость.
Существует еще один термин, который часто используют производственники и продавцы. Это «коэффициент прибыльности». Он исчисляется в процентах по той же формуле и, по сути, является той же маржой. Просто существуют люди, которые используют термин «коэффициент прибыльности» для выражения маржи в процентах, а термин «маржа» — для выражения той же маржи в денежном эквиваленте, либо под «маржой» имеют в виду только прибыль на единицу продукта, а коэффициент прибыльности считают по всем продажам (производственной партии ли, или за отчетный период) в целом
Поэтому так важно между коллегами и партнерами сразу определяться с конкретикой для используемых названий.
Маржа и наценка: важно знать разницу
Когда вам говорят словосочетание «маржинальность равна 146%», вы должны понимать, что это абсурд, и речь идет совсем не о марже. Большая вероятность, что речь идет о наценке.
Пример
Маржинальность никогда не может быть выше 99%!
Наценка может быть 150%, 200%, 500%, 1000% и так далее.
Для чего считают маржу? Это показатель прибыльности ваших отдельных сделок, вашего бизнеса в целом. Он помогает анализировать и принимать правильные решения в управленческих, маркетинговых, логистических и стратегических задачах. На практике маржу просчитывают по отдельности по многим параметрам. Разные виды товаров или услуг одного и того же предприятия, разные партии одного и того же товара (допустим, проданные по разным отпускным ценам). Отдельно просчитываются случаи продаж единиц товара по нетипичной цене (нетипично высокой или нетипично низкой). Кроме того, в сложных производственных системах есть разновидности издержек, некоторые из них переменные (иногда их включают в себестоимость, иногда — нет), а некоторые постоянные.
Вот почему так важно, чтобы у вас с коллегами было единое понимание, какую именно маржу и как вы будете считать.
Маржа и валовая прибыль: в чем разница

фото с сайта dela.biz
Финансовые показатели, которые отражают динамику развития компании, достаточно похожи между собой. Это вызывает путаницу. В то же время различие между маржей и прибылью – ключевыми характеристиками оценки деятельности компании – есть.
Так, первый из них учитывает только производственные издержки. Из их совокупности складывается себестоимость товара. Прибыль подразумевает более широкий анализ показателей – при ее расчете учитывается вся совокупность расходов и поступлений, которые возникали во время производственного процесса и при реализации продукции.
Допустим, у вас есть частная фирма, которая занимается производством шарнирных кукол. Для их изготовления вам понадобится расходный материал (например, папье-маше, самозатвердевающая глина), оборудование (набор инструментов), краски и аксессуары. Все то, что будет потрачено на производство одной куклы – это храктеристики, из которых будет формироваться себестоимость предмета. Представим, что расходный материал обошелся вам в 20$. Формируя отпускную цену готового изделия, вы учитываете эксплуатацию инструментов (а при использовании специального оборудования, например, печи для закрепления формы, амортизационные расходы приборов), время, потраченное вами на разработку проекта и его воплощения. Кроме того, вы наверняка не забудете оценить художественную ценность своей работы, прибавив к стоимости, основанной на фактических данных, некие субъективные критерии. В итоге у вас получится цифра, которая превышает 20$ в несколько раз – например, 200$.
По сути, разница между отпускной ценой и фактическими расходами представляет собой заработанную вами прибыль. Однако это не совсем так. С точки зрения терминологии, такое понятие как «прибыль» учитывает не два показателя, а намного больше.
Если вернуться к примеру с куклой, то при подсчете реального дохода вы, условно, должны будете учитывать количество чая, которое выпили при лепке и оформлении изделия, оплату интернета, задействованного в рекламе продукции, транспортные расходы, связанные с пересылкой товара в случае адресата, расположенного в другом городе и т.д. Только после совокупного учета всех данных, вы сможете сделать вывод относительно того, сколько смогли заработать. В этом и заключается отличие прибыли от маржи.
Анализ деятельности компании показывает, что эти два показателя всегда прямо пропорциональны. Чем больше один, тем выше значение другого в конкретном отчетном периоде. В то же время маржа, по понятным причинам, всегда выше прибыли.
Operating Cash Flow Margin vs. Operating Margin
The operating cash flow margin is unlike the operating margin. The operating margin includes depreciation and amortization expenses. However, operating cash flow margin adds back non-cash expenses, such as depreciation.
Operating margin is calculated as operating income divided by revenue. This similar to operating cash flow margin except it uses operating income. Operating cash flow margin uses operating cash flow and not operating income.
Free cash flow margin is another cash margin measure, where it also adds in capital expenditures. In capital intensive industries, with a high ratio of fixed to variable costs, a small increase in sales can lead to a large increase in operating cash flows, thanks to operational leverage.
Operating Cash Flow Margin Example
Operating Cash Flow = Net Income + Non-cash Expenses (Depreciation and Amortization) + Change in Working Capital
Assuming company ABC recorded the following information for 2018 business activities:
Sales = $5,000,000
Depreciation = $100,000
Amortization = $125,000
Other Non-cash Expenses = $45,000
Working Capital = $1,000,000
Net Income = $2,000,000
And recorded the following information for 2019’s business activities:
Sales = $5,300,000
Depreciation = $110,000
Amortization = $130,000
Other Non-cash Expenses = $55,000
Working Capital = $1,300,000
Net Income = $2,100,000
We calculate the cash flow from operating activities for the 2019 as:
Cash Flow From Operating Activities = $2,100,00 + ($110,000 + $130,000 + $55,000) + ($1,300,000 — $1,000,000) = $2,695,000
To arrive at the operating cash flow margin, this number is divided by sales:
Operating Cash Flow Margin = $2,695,000 / $5,300,000 = 50.8%
Увеличение маржи операционной прибыли
Как уже говорилось, накладные расходы компании не учитываются в валовой прибыли. Это число говорит о том, является ли продукт жизнеспособным вариантом продажи с достаточно высокой маржой прибыли для успеха компании. Все остальные операционные расходы влияют на маржу операционной прибыли и, в конечном итоге, на чистую прибыль компании.
Эти расходы включают аренду офиса и коммунальные услуги, оборудование персонала и расходы на выполнение. Например, если компания продает 100 000 долларов США в продуктах с COGS 10000 долларов США, ее валовая прибыль составляет 90 процентов. Если для выполнения операций требуется еще 50 000 долл. До уплаты налогов и процентов, маржа операционной прибыли составляет 40 процентов: (100 000–10 000–50 000 долл. США) / 100.
Можно уменьшить валовую прибыль и при этом увеличить операционную прибыль. Возьмите пример выше. Предположим, что стоимость создания продуктов на макроуровне увеличилась с 10 000 до 20 000 долларов. это означает, что валовая прибыль снизится с 90 до 80 процентов. Но представьте, если операционные расходы сократились на 20 000 долларов.
Это означает, что маржа операционной прибыли увеличится с 40% до 60% [(100 000 — 20 000 долл. США — 30 0000 долл. / 100]. Одной из причин может быть то, что компания нашла способ рационализировать ежедневные операции. Возможно, вместо найма подрядчиков сотрудники делали онлайн-маркетинг вместо телефонных банков или оптимизировали системы управления запасами с помощью облачных решений.Есть бесконечное множество возможностей, которые могут снизить эксплуатационные расходы и увеличить маржу операционной прибыли.
Gross Margin vs. Contribution Margin Example
If total revenue for a company was $2 million and the cost of goods sold was $1.5 million, gross margin would equal revenue less COGS, which is $500,000, or $2,000,000 — $1,500,000. As a percentage (gross profit margin), it’s 25%, or (2,000,0000 — $1,500,000) / 2,000,000.
As an example of contribution margin, consider total sales or revenue from an item that a company produces equals $10,000 while the variable costs for the item equal $6,000. The contribution margin is calculated by subtracting the variable costs from the revenue generated from sales of the item and dividing the result by revenue, or (sales — variable costs) / sales. Thus, the contribution margin in our example is 40%, or ($10,000 — $6,000) / $10,000.
The contribution margin is not intended to be an all-encompassing measure of a company’s profitability. However, the contribution margin can be used to examine variable production costs. The contribution margin can also be used to evaluate the profitability of an item and to calculate how to improve its profitability, either by reducing variable production costs or by increasing the item’s price.
Types of Profit Margin
Let’s look more closely at the different varieties of profit margins.
Gross Profit Margin
Gross profit margin: Start with sales and take out costs directly related to creating or providing the product or service like raw materials, labor, and so on—typically bundled as «cost of goods sold,” “cost of products sold,” or “cost of sales” on the income statement—and you get gross margin. Done on a per-product basis, gross margin is most useful for a company analyzing its product suite (though this data isn’t shared with the public), but aggregate gross margin does show a company’s rawest profitability picture. As a formula:
Gross profit margin=Net sales − COGSNet saleswhere:\begin{aligned} &\textit{Gross profit margin}=\frac{\textit{Net sales }-\textit{ COGS}}{\textit{Net sales}}\\ &\textbf{where:}\\ &\textit{COGS}=\text{cost of goods sold} \end{aligned}Grossprofitmargin=NetsalesNetsales−COGSwhere:
Operating Profit Margin
Operating Profit Margin (or just operating margin): By subtracting selling, general and administrative, or operating expenses, from a company’s gross profit number, we get operating profit margin, also known as earnings before interest and taxes, or EBIT. Resulting in an income figure that’s available to pay the business’ debt and equity holders, as well as the tax department, it’s profit from a company’s main, ongoing operations. it’s frequently used by bankers and analysts to value an entire company for potential buyouts. As a formula:
Operating Profit Margin=Operating IncomeRevenue × 1\textbf{Operating Profit Margin}=\frac{\textbf{Operating Income}}{\textbf{Revenue}}\ \mathbf{\times\ 100}OperatingProfitMargin=RevenueOperatingIncome×1
Pretax Profit Margin
Pretax profit margin: Take operating income and subtract interest expense while adding any interest income, adjust for non-recurring items like gains or losses from discontinued operations, and you’ve got pre-tax profit, or earnings before taxes (EBT); then divide by revenue, and you’ve got the pretax profit margin.
The major profit margins all compare some level of residual (leftover) profit to sales. For instance, a 42% gross margin means that for every $100 in revenue, the company pays $58 in costs directly connected to producing the product or service, leaving $42 as gross profit.
Understanding the Operating Cash Flow Margin
Operating cash flow margin measures how efficiently a company converts sales into cash. It is a good indicator of earnings quality because it only includes transactions that involve the actual transfer of money.
Because cash flow is driven by revenues, overhead and operating efficiency, it can be very telling, especially when comparing performance to competitors in the same industry. Has operating cash flow turned negative because the company is investing in its operations to make them even more profitable? Or does the company need an injection of outside capital to buy time to continue operating in a desperate attempt to turn around the business?
Just as companies can improve operating cash flow margin, by using working capital more efficiently, they can also temporarily flatter operating cash flow margin by delaying the payment of accounts payable, chasing customers for payment or running down inventory. But if a company’s operating cash flow margin is increasing from year to year, it indicates its free cash flow is improving, as is its ability to expand its asset base and create long-term value for shareholders.
What Is Operating Margin?
Operating margin additionally subtracts all overhead and operational expenses from revenues, indicating the amount of profit the company has left before figuring in the expenses of taxes and interest. For this reason, operating margin is sometimes referred to as EBIT, or earnings before interest and tax.
Operating margin is calculated with the same formula as gross margin, simply subtracting the additional costs from revenue before dividing by the revenue figure. Operating expenses include items such as wages, marketing costs, facility costs, vehicle costs, depreciation, and amortization of equipment. Analyzing a company’s historical operating margins can be a good way to tell if recent earnings growth in the business is likely to last.
Understanding Operating Margin
A company’s operating margin, also known as return on sales, is a good indicator of how well it is being managed and how risky it is. It shows the proportion of revenues that are available to cover non-operating costs, like paying interest, which is why investors and lenders pay close attention to it.
Highly variable operating margins are a prime indicator of business risk. By the same token, looking at a company’s past operating margins is a good way to gauge whether a company’s performance has been getting better. Operating margin can improve through better management controls, more efficient use of resources, improved pricing, and more effective marketing.
In its essence, operating margin is how much profit a company makes from its core business in relation to its total revenues. This allows investors to see if a company is generating income primarily from its core operations or from other means, such as investing.
General Motors (GM) was a prime example of this. In the 1980s and 1990s, GM was making the bulk of its profits from financing cars as opposed to making and selling actual cars, its core operations. Therefore, its operating margins were very low. Since then, its automotive business generates more income than its financing business.
How to calculate net profit margin

The formula for this calculation is revenue minus the cost of goods sold, operating expenses, other expenses, interest (e.g. on debt), and taxes. Again, this is divided by total revenue and multiplied by 100 to get your margin percentage, so it looks like:
| Net Profit Margin | = | Net Income | x | 100 | ||
| ‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾ | ||||||
| Total Revenue |
Your net margin can be negative or positive, with negative percentages showing where your company failed to be profitable over a certain timeframe.
Say your company makes $10,000 in sales for the quarter. Your products cost you $8,000 and you had to factor in costs for overheads and taxes of $1,000.
Your calculations to reach the net margin percentage would look like this:
$10,000 – ($8,000 + $1,000) = $1,000 (this is your net income)
$1,000 ÷ $10,000 = 0.1
0.1 × 100 = 10%
In this example, your net profit margin is 10%, which tells you how much of your total sales revenue is profit.
Some companies opt for sales and pricing strategies like lowering their net profit margin and driving exponentially more sales to increase their total net profits.
This looks great on paper – but unless you’re Walmart, a low cost/high volume tactic can be a risky approach that serves only to damage your brand image and position you as a “cheap” company (also a little like Walmart!).
Основные виды
Данный термин используется во многих областях деятельности человека – существует большое количество ее разновидностей. Рассмотрим самые широко используемые.
Валовая (Gross Profit Margin)
Валовая или гросс маржа – это процент от всего объема выручки, оставшейся после переменных затрат. Такими затратами могут быть закупка сырья и материалов для производства, выплата заработной платы работникам, трата средств на сбыт товаров и т. д. Она характеризует общую работу предприятия, определяет его чистую прибыль, а также используется для подсчета других величин.
Операционная (Operating profit margin)
Операционная маржа – это отношение операционной прибыли предприятия к его доходу. Она указывает на количество выручки в процентном соотношении, которая остается у компании после учета себестоимости товара, а также других сопутствующих расходов.
Важно! Высокие показатели говорят о хорошей эффективности компании. Но стоит быть на чеку, потому что этими цифрами можно манипулировать.
Чистая (Net Profit Margin)
Чистая маржа – это отношение чистой прибыли предприятия к его выручке. Она отображает, какое количество денежных единиц прибыли предприятие получает из одной денежной единицы выручки. После ее расчета становится понятно, насколько успешно компания справляется со своими расходами.
Зная чистую прибыль, можно посчитать маржинальность или норму рентабельности бизнеса – это дает возможность в процентах оценить соотношение этой прибыли к вложенному капиталу.
Нужно отметить, что на значение конечного показателя влияет направление работы предприятия. Например, фирмы, работающие в сфере розничной торговли, обычно имеют достаточно маленькие цифры, а крупные производственные предприятия обладают довольно таки высокими цифрами.
Процентная
Процентная маржа – это один из важных показателей деятельности банка, она характеризует соотношение его доходных и расходных частей. С ее помощью определяют доходность операций по ссудам и то, может ли банк покрыть свои издержки.
Данная разновидность бывает абсолютной и относительной. На ее величину могут влиять темпы инфляции, разного рода активные операции, отношение между капиталом банка и ресурсами, которые привлечены извне и т. д.
Вариационная
Вариационная маржа (ВМ)– это величина, которая обозначает возможную прибыль или убыток на торговых площадках. Также это число, по которому может увеличиваться или уменьшаться объем денежных средств, взятых под залог во время торговой сделки.
Если трейдер правильно спрогнозировал движение рынка, то данная величина будет положительной. В противоположной ситуации она будет отрицательной.
Когда сессия заканчивается, то набежавшая ВМ прибавляется к счету или наоборот – аннулируется.
Если трейдер держит свою позицию только на протяжении одной сессии, то итоги торговой сделки будут одинаковыми с ВМ.
А если трейдер держит свою позицию продолжительное время, она будет приплюсовываться ежедневно, и в конечном счете ее показатели не будут одинаковыми с итогом по сделке.
Просмотрите видео о том, что такое маржа:
About This Article
Co-authored by:
Business Advisor
This article was co-authored by Michael R. Lewis. Michael R. Lewis is a retired corporate executive, entrepreneur, and investment advisor in Texas. He has over 40 years of experience in business and finance, including as a Vice President for Blue Cross Blue Shield of Texas. He has a BBA in Industrial Management from the University of Texas at Austin. This article has been viewed 1,409,430 times.
6 votes — 67%
Co-authors: 18
Updated: March 29, 2019
Views: 1,409,430
Categories: Featured Articles | Accounting
To calculate gross profit margin, start by subtracting the cost of goods sold from the net sales. Then, divide the difference by the net sales to find the gross profit margin. If you’re not sure what the net sales and cost of goods sold are, you can look them up on the company’s income statement. For more tips from our Financial co-author, like how to interpret gross profit margin, scroll down!
Did this summary help you?YesNo
Español:calcular el margen bruto de ganancias
Português:Calcular a Margem de Lucro Bruto
Deutsch:Die Bruttogewinnspanne errechnen
Italiano:Calcolare il Margine Lordo
中文:计算毛利率
Русский:вычислить коэффициент валовой прибыли
Français:calculer la marge bénéficiaire brute
ไทย:คำนวณกำไรขั้นต้น
Bahasa Indonesia:Menghitung Margin Laba Kotor
العربية:حساب هامش إجمالي الربح
Nederlands:Brutowinstmarge berekenen
Tiếng Việt:Tính Tỷ lệ Lợi nhuận Gộp
हिन्दी:सकल लाभ की गणना करें
Другие виды маржи
Современные специалисты подразделяют маржу на множество разновидностей. Так, например, в кредитовании известно такое понятие, как вариационная маржа, представляющее собой размер компенсации, которую кредитная организация или один из участников биржевой сделки выплачивает, когда сделка претерпевает изменения финансовой направленности.
Валовая маржа, речь о которой шла выше, считается одним из важнейших коэффициентов анализа. Этот показатель используют во многих областях для менеджмента и контроллинга.
Два термина, рассматриваемые в зависимости — фронт маржа и бэк маржа — непрерывно связаны с друг другом. Первая из них представляет собой получение дохода с наценки, а вторая — доход от бонусов, акций или скидок. Главное отличие между этими видами маржи — это то, что при использовании бэк-маржи прибыль приходит от поставщиков, но потом, то есть, «задним» числом.
Операционной маржей называется сумма потерь или доходов предприятия только от его главной деятельности.
Коммерческая маржа — это коэффициент, не бывающий ни от чего не зависимым. Его величина основывается на показателях торговой наценки, собственной стоимости товара и количестве его продаж.
Свободной маржей называется реальное отличие между балансом счета трейдера и суммарном задатке по всем открытым позициям.
Контрибуционной маржей считается разница между валовой прибылью и суммой тех затрат, которые постоянно изменяются.
 Маржа на Форекс — это временное залоговое сотрудничество, в результате которого человек может получить на некоторое время финансы, необходимые ему для проведения операции.
Маржа на Форекс — это временное залоговое сотрудничество, в результате которого человек может получить на некоторое время финансы, необходимые ему для проведения операции.
Чтобы правильно производить математические расчеты для каждого конкретного случая, нужно хорошо разбираться в специальных формулах. Кроме того, профессионалы в каждой из этих областей должны не только разбираться в расчете тех или иных показателей, но и владеть умением давать им верную оценку, для чего им понадобится множество специальных знаний и практического опыта.
Comparing Gross Margin and Operating Margin
There are plenty of similarities between gross margin and operating margin. Both are representations of how efficiently a company is able to generate profit by expressing it through a per-sale basis. Higher margins are considered better than lower margins. Both can be compared between similar competitors, but not across different industries.
Since operational costs such as salaries and advertising are more easily adjusted than the usually fixed costs of production, companies scrutinize their operating expenses for ways to cut costs efficiently, in an effort to increase their profit margins. The operating margin calculation, as it is done without including costs of financing or tax expenses, also provides a company with a clear indication of whether it has a solid enough profit position to take on additional financing to expand.
Operating margin is a more significant bottom-line number for investors than gross margin. Comparisons between two companies’ operating margins with similar business models and annual sales are considered to be more telling.
Gross profit margin is almost always higher than the operating margin because there are fewer costs to subtract from gross income. Gross margin offers a more specific look at how well a company is managing the resources that directly contribute to the production of its salable goods and services.
Hypothetical Example
Imagine a company that has the following numbers reported on its income statement:
- Revenue: $100,000
- Operating costs: $20,000
- COGS or cost of goods sold: $10,000
- Tax liability: $14,000
- Net profits: $56,000
Net profit margin is thus 0.56 or 56% ($56,000/$100,000) x 100. A 56 percent profit margin indicates the company earns 56 cents in profit for every dollar it collects.
Let’s take another hypothetical example using the made-up Jazz Music Shop’s FY 2025 income statement.
Here, we can gather all of the information we need to plug into the net profit margin equation. We take our total revenue of $6,400 and deduct variable costs of $1,700 as well as fixed costs of $350 to arrive at a net income of $4,350 for the period. If Jazz Music Shop also had to pay interest and taxes, that too would have been deducted from revenues.
The net profit margin is calculated by taking the ratio of net income to revenue. Net profit margin is calculated as follows:
- 4350
- $4,350 / $6,400 x 100 = .68 x 100 = 68%
$435$64∗1=.68∗1=68%\$4350 / \$6400 * 100 = 0.68 * 100 = 68\%$435$64∗1=.68∗1=68%
Analysis
The gross profit method is an important concept because it shows management and investors how efficiently the business can produce and sell products. In other words, it shows how profitable a product is.
The concept of GP is particularly important to cost accountants and management because it allows them to create budgets and forecast future activities. For instance, Monica’s GP was $650,000. This means if she wants to be profitable for the year, all of her other costs must be less than $650,000. Conversely, Monica can also view the $650,000 as the amount of money that can be put toward other business expenses or expansion into new markets.
Investors are typically interested in GP as a percentage because this allows them to compare margins between companies no matter their size or sales volume. For instance, an investor can see Monica’s 65 percent margin and compare it to Ralph Lauren’s margin even though RL is a billion dollar company. It also allows investors a chance to see how profitable the company’s core business activities are.
General Motors is a good example of this back in the 1990s. GM had a low margin and wasn’t making much money one each car they were producing, but GM was profitable. Why? Because GM’s financing services were raking in the money. In other words, GM was making more money financing cars like a bank than they were producing cars like a manufacturer. Investors want to know how healthy the core business activities are to gauge the quality of the company.
They also use a gross profit margin calculator to measure scalability. Monica’s investors can run different models with her margins to see how profitable the company would be at different sales levels. For instance, they could measure the profits if 100,000 units were sold or 500,000 units were sold by multiplying the potential number of units sold by the sales price and the GP margin.
Break EvenWACC
Contents